MNN-Export für YOLO26-Modelle und Bereitstellung
MNN
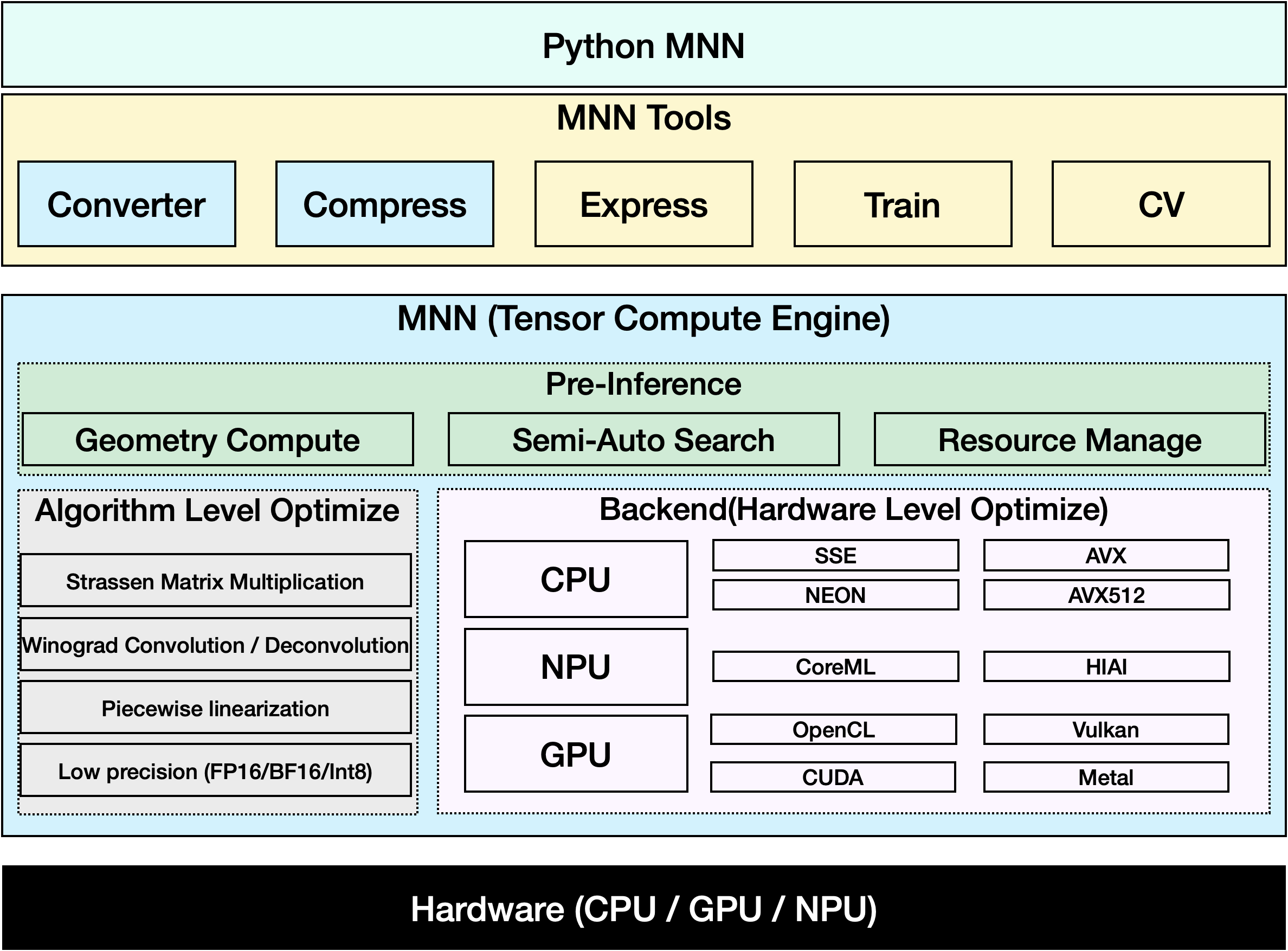
MNN ist ein hocheffizientes und leichtgewichtiges Deep-Learning-Framework. Es unterstützt Inferenz und Training von Deep-Learning-Modellen und bietet eine branchenführende Leistung für Inferenz und Training auf dem Gerät. Derzeit ist MNN in mehr als 30 Apps von Alibaba Inc. integriert, wie z. B. Taobao, Tmall, Youku, DingTalk, Xianyu usw., die mehr als 70 Anwendungsszenarien abdecken, wie z. B. Live-Übertragung, Kurzvideoaufnahme, Suchempfehlung, Produktsuche per Bild, interaktives Marketing, Aktienverteilung, Sicherheitsrisikokontrolle. Darüber hinaus wird MNN auch auf eingebetteten Geräten wie IoT eingesetzt.
Ansehen: Wie man Ultralytics YOLO26 in das MNN-Format exportiert | Beschleunigung der Inferenz auf mobilen Geräten📱
Export nach MNN: Konvertierung Ihres YOLO26-Modells
Sie können die Modellkompatibilität und Bereitstellungsflexibilität erweitern, indem Sie Ultralytics YOLO-Modelle in das MNN-Format konvertieren. Diese Konvertierung optimiert Ihre Modelle für mobile und eingebettete Umgebungen und gewährleistet eine effiziente Leistung auf Geräten mit beschränkten Ressourcen.
Installation
Um die erforderlichen Pakete zu installieren, führen Sie Folgendes aus:
Installation
# Install the required package for YOLO26 and MNN
pip install ultralytics
pip install MNN
Nutzung
Alle Ultralytics YOLO26-Modelle sind so konzipiert, dass sie den Export sofort unterstützen, was die Integration in Ihren bevorzugten Bereitstellungs-Workflow erleichtert. Sie können die vollständige Liste der unterstützten Exportformate und Konfigurationsoptionen einsehen, um die beste Einrichtung für Ihre Anwendung zu wählen.
Nutzung
from ultralytics import YOLO
# Load the YOLO26 model
model = YOLO("yolo26n.pt")
# Export the model to MNN format
model.export(format="mnn") # creates 'yolo26n.mnn'
# Load the exported MNN model
mnn_model = YOLO("yolo26n.mnn")
# Run inference
results = mnn_model("https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg")
# Export a YOLO26n PyTorch model to MNN format
yolo export model=yolo26n.pt format=mnn # creates 'yolo26n.mnn'
# Run inference with the exported model
yolo predict model='yolo26n.mnn' source='https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg'
Export-Argumente
| Argument | Typ | Standard | Beschreibung |
|---|---|---|---|
format | str | 'mnn' | Zielformat für das exportierte Modell, das die Kompatibilität mit verschiedenen Deployment-Umgebungen definiert. |
imgsz | int oder tuple | 640 | Gewünschte Bildgröße für die Modelleingabe. Kann eine ganze Zahl für quadratische Bilder oder ein Tupel (height, width) für bestimmte Abmessungen sein. |
half | bool | False | Aktiviert die FP16-Quantisierung (halbe Präzision), wodurch die Modellgröße reduziert und potenziell die Inferenz auf unterstützter Hardware beschleunigt wird. |
int8 | bool | False | Aktiviert die INT8-Quantisierung, wodurch das Modell weiter komprimiert und die Inferenz mit minimalem Genauigkeitsverlust beschleunigt wird, hauptsächlich für Edge-Geräte. |
batch | int | 1 | Gibt die Batch-Inferenzgröße des Exportmodells oder die maximale Anzahl von Bildern an, die das exportierte Modell gleichzeitig verarbeitet predict Modus. |
device | str | None | Gibt das Gerät für den Export an: GPU (device=0), CPU (device=cpu), MPS für Apple Silicon (device=mps), oder Auto-Modus mit angegebener Auslastungsfraktion ( |
Weitere Informationen zum Exportprozess finden Sie auf der Ultralytics-Dokumentationsseite zum Exportieren.
MNN-Only Inferenz
Es wurde eine Funktion implementiert, die sich ausschließlich auf MNN für die YOLO26-Inferenz und -Vorverarbeitung stützt und sowohl Python- als auch C++-Versionen für eine einfache Bereitstellung in jedem Szenario bietet.
MNN
import argparse
import MNN
import MNN.cv as cv2
import MNN.numpy as np
def inference(model, img, precision, backend, thread):
config = {}
config["precision"] = precision
config["backend"] = backend
config["numThread"] = thread
rt = MNN.nn.create_runtime_manager((config,))
# net = MNN.nn.load_module_from_file(model, ['images'], ['output0'], runtime_manager=rt)
net = MNN.nn.load_module_from_file(model, [], [], runtime_manager=rt)
original_image = cv2.imread(img)
ih, iw, _ = original_image.shape
length = max((ih, iw))
scale = length / 640
image = np.pad(original_image, [[0, length - ih], [0, length - iw], [0, 0]], "constant")
image = cv2.resize(
image, (640, 640), 0.0, 0.0, cv2.INTER_LINEAR, -1, [0.0, 0.0, 0.0], [1.0 / 255.0, 1.0 / 255.0, 1.0 / 255.0]
)
image = image[..., ::-1] # BGR to RGB
input_var = image[None]
input_var = MNN.expr.convert(input_var, MNN.expr.NC4HW4)
output_var = net.forward(input_var)
output_var = MNN.expr.convert(output_var, MNN.expr.NCHW)
output_var = output_var.squeeze()
# output_var shape: [84, 8400]; 84 means: [cx, cy, w, h, prob * 80]
cx = output_var[0]
cy = output_var[1]
w = output_var[2]
h = output_var[3]
probs = output_var[4:]
# [cx, cy, w, h] -> [y0, x0, y1, x1]
x0 = cx - w * 0.5
y0 = cy - h * 0.5
x1 = cx + w * 0.5
y1 = cy + h * 0.5
boxes = np.stack([x0, y0, x1, y1], axis=1)
# ensure ratio is within the valid range [0.0, 1.0]
boxes = np.clip(boxes, 0, 1)
# get max prob and idx
scores = np.max(probs, 0)
class_ids = np.argmax(probs, 0)
result_ids = MNN.expr.nms(boxes, scores, 100, 0.45, 0.25)
print(result_ids.shape)
# nms result box, score, ids
result_boxes = boxes[result_ids]
result_scores = scores[result_ids]
result_class_ids = class_ids[result_ids]
for i in range(len(result_boxes)):
x0, y0, x1, y1 = result_boxes[i].read_as_tuple()
y0 = int(y0 * scale)
y1 = int(y1 * scale)
x0 = int(x0 * scale)
x1 = int(x1 * scale)
# clamp to the original image size to handle cases where padding was applied
x1 = min(iw, x1)
y1 = min(ih, y1)
print(result_class_ids[i])
cv2.rectangle(original_image, (x0, y0), (x1, y1), (0, 0, 255), 2)
cv2.imwrite("res.jpg", original_image)
if __name__ == "__main__":
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument("--model", type=str, required=True, help="the yolo26 model path")
parser.add_argument("--img", type=str, required=True, help="the input image path")
parser.add_argument("--precision", type=str, default="normal", help="inference precision: normal, low, high, lowBF")
parser.add_argument(
"--backend",
type=str,
default="CPU",
help="inference backend: CPU, OPENCL, OPENGL, NN, VULKAN, METAL, TRT, CUDA, HIAI",
)
parser.add_argument("--thread", type=int, default=4, help="inference using thread: int")
args = parser.parse_args()
inference(args.model, args.img, args.precision, args.backend, args.thread)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <MNN/ImageProcess.hpp>
#include <MNN/expr/Module.hpp>
#include <MNN/expr/Executor.hpp>
#include <MNN/expr/ExprCreator.hpp>
#include <MNN/expr/Executor.hpp>
#include <cv/cv.hpp>
using namespace MNN;
using namespace MNN::Express;
using namespace MNN::CV;
int main(int argc, const char* argv[]) {
if (argc < 3) {
MNN_PRINT("Usage: ./yolo26_demo.out model.mnn input.jpg [forwardType] [precision] [thread]\n");
return 0;
}
int thread = 4;
int precision = 0;
int forwardType = MNN_FORWARD_CPU;
if (argc >= 4) {
forwardType = atoi(argv[3]);
}
if (argc >= 5) {
precision = atoi(argv[4]);
}
if (argc >= 6) {
thread = atoi(argv[5]);
}
MNN::ScheduleConfig sConfig;
sConfig.type = static_cast<MNNForwardType>(forwardType);
sConfig.numThread = thread;
BackendConfig bConfig;
bConfig.precision = static_cast<BackendConfig::PrecisionMode>(precision);
sConfig.backendConfig = &bConfig;
std::shared_ptr<Executor::RuntimeManager> rtmgr = std::shared_ptr<Executor::RuntimeManager>(Executor::RuntimeManager::createRuntimeManager(sConfig));
if(rtmgr == nullptr) {
MNN_ERROR("Empty RuntimeManger\n");
return 0;
}
rtmgr->setCache(".cachefile");
std::shared_ptr<Module> net(Module::load(std::vector<std::string>{}, std::vector<std::string>{}, argv[1], rtmgr));
auto original_image = imread(argv[2]);
auto dims = original_image->getInfo()->dim;
int ih = dims[0];
int iw = dims[1];
int len = ih > iw ? ih : iw;
float scale = len / 640.0;
std::vector<int> padvals { 0, len - ih, 0, len - iw, 0, 0 };
auto pads = _Const(static_cast<void*>(padvals.data()), {3, 2}, NCHW, halide_type_of<int>());
auto image = _Pad(original_image, pads, CONSTANT);
image = resize(image, Size(640, 640), 0, 0, INTER_LINEAR, -1, {0., 0., 0.}, {1./255., 1./255., 1./255.});
image = cvtColor(image, COLOR_BGR2RGB);
auto input = _Unsqueeze(image, {0});
input = _Convert(input, NC4HW4);
auto outputs = net->onForward({input});
auto output = _Convert(outputs[0], NCHW);
output = _Squeeze(output);
// output shape: [84, 8400]; 84 means: [cx, cy, w, h, prob * 80]
auto cx = _Gather(output, _Scalar<int>(0));
auto cy = _Gather(output, _Scalar<int>(1));
auto w = _Gather(output, _Scalar<int>(2));
auto h = _Gather(output, _Scalar<int>(3));
std::vector<int> startvals { 4, 0 };
auto start = _Const(static_cast<void*>(startvals.data()), {2}, NCHW, halide_type_of<int>());
std::vector<int> sizevals { -1, -1 };
auto size = _Const(static_cast<void*>(sizevals.data()), {2}, NCHW, halide_type_of<int>());
auto probs = _Slice(output, start, size);
// [cx, cy, w, h] -> [y0, x0, y1, x1]
auto x0 = cx - w * _Const(0.5);
auto y0 = cy - h * _Const(0.5);
auto x1 = cx + w * _Const(0.5);
auto y1 = cy + h * _Const(0.5);
auto boxes = _Stack({x0, y0, x1, y1}, 1);
// ensure ratio is within the valid range [0.0, 1.0]
boxes = _Maximum(boxes, _Scalar<float>(0.0f));
boxes = _Minimum(boxes, _Scalar<float>(1.0f));
auto scores = _ReduceMax(probs, {0});
auto ids = _ArgMax(probs, 0);
auto result_ids = _Nms(boxes, scores, 100, 0.45, 0.25);
auto result_ptr = result_ids->readMap<int>();
auto box_ptr = boxes->readMap<float>();
auto ids_ptr = ids->readMap<int>();
auto score_ptr = scores->readMap<float>();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
auto idx = result_ptr[i];
if (idx < 0) break;
auto x0 = box_ptr[idx * 4 + 0] * scale;
auto y0 = box_ptr[idx * 4 + 1] * scale;
auto x1 = box_ptr[idx * 4 + 2] * scale;
auto y1 = box_ptr[idx * 4 + 3] * scale;
// clamp to the original image size to handle cases where padding was applied
x1 = std::min(static_cast<float>(iw), x1);
y1 = std::min(static_cast<float>(ih), y1);
auto class_idx = ids_ptr[idx];
auto score = score_ptr[idx];
rectangle(original_image, {x0, y0}, {x1, y1}, {0, 0, 255}, 2);
}
if (imwrite("res.jpg", original_image)) {
MNN_PRINT("result image write to `res.jpg`.\n");
}
rtmgr->updateCache();
return 0;
}
Zusammenfassung
In diesem Leitfaden stellen wir vor, wie das Ultralytics YOLO26-Modell nach MNN exportiert und MNN für die Inferenz verwendet wird. Das MNN-Format bietet eine hervorragende Leistung für Edge-AI-Anwendungen und ist somit ideal für die Bereitstellung von Computer-Vision-Modellen auf ressourcenbeschränkten Geräten.
Weitere Informationen zur Verwendung finden Sie in der MNN-Dokumentation.
FAQ
Wie exportiere ich Ultralytics YOLO26-Modelle in das MNN-Format?
Um Ihr Ultralytics YOLO26-Modell in das MNN-Format zu exportieren, folgen Sie diesen Schritten:
Export
from ultralytics import YOLO
# Load the YOLO26 model
model = YOLO("yolo26n.pt")
# Export to MNN format
model.export(format="mnn") # creates 'yolo26n.mnn' with fp32 weight
model.export(format="mnn", half=True) # creates 'yolo26n.mnn' with fp16 weight
model.export(format="mnn", int8=True) # creates 'yolo26n.mnn' with int8 weight
yolo export model=yolo26n.pt format=mnn # creates 'yolo26n.mnn' with fp32 weight
yolo export model=yolo26n.pt format=mnn half=True # creates 'yolo26n.mnn' with fp16 weight
yolo export model=yolo26n.pt format=mnn int8=True # creates 'yolo26n.mnn' with int8 weight
Detaillierte Exportoptionen finden Sie auf der Seite Export in der Dokumentation.
Wie führe ich Vorhersagen mit einem exportierten YOLO26 MNN-Modell durch?
Um mit einem exportierten YOLO26 MNN-Modell Vorhersagen zu treffen, verwenden Sie die predict Funktion aus der YOLO-Klasse.
Vorhersagen
from ultralytics import YOLO
# Load the YOLO26 MNN model
model = YOLO("yolo26n.mnn")
# Export to MNN format
results = model("https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg") # predict with `fp32`
results = model("https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg", half=True) # predict with `fp16` if device support
for result in results:
result.show() # display to screen
result.save(filename="result.jpg") # save to disk
yolo predict model='yolo26n.mnn' source='https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg' # predict with `fp32`
yolo predict model='yolo26n.mnn' source='https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg' --half=True # predict with `fp16` if device support
Welche Plattformen werden für MNN unterstützt?
MNN ist vielseitig und unterstützt verschiedene Plattformen:
- Mobil: Android, iOS, Harmony.
- Eingebettete Systeme und IoT-Geräte: Geräte wie Raspberry Pi und NVIDIA Jetson.
- Desktops und Server: Linux, Windows und macOS.
Wie kann ich Ultralytics YOLO26 MNN-Modelle auf mobilen Geräten bereitstellen?
Um Ihre YOLO26-Modelle auf mobilen Geräten bereitzustellen:
- Build für Android: Folgen Sie der MNN Android Anleitung.
- Build für iOS: Folgen Sie der MNN iOS Anleitung.
- Build für Harmony: Folgen Sie der MNN Harmony Anleitung.