Xuất MNN cho các mô hình YOLO26 và Triển khai
MNN
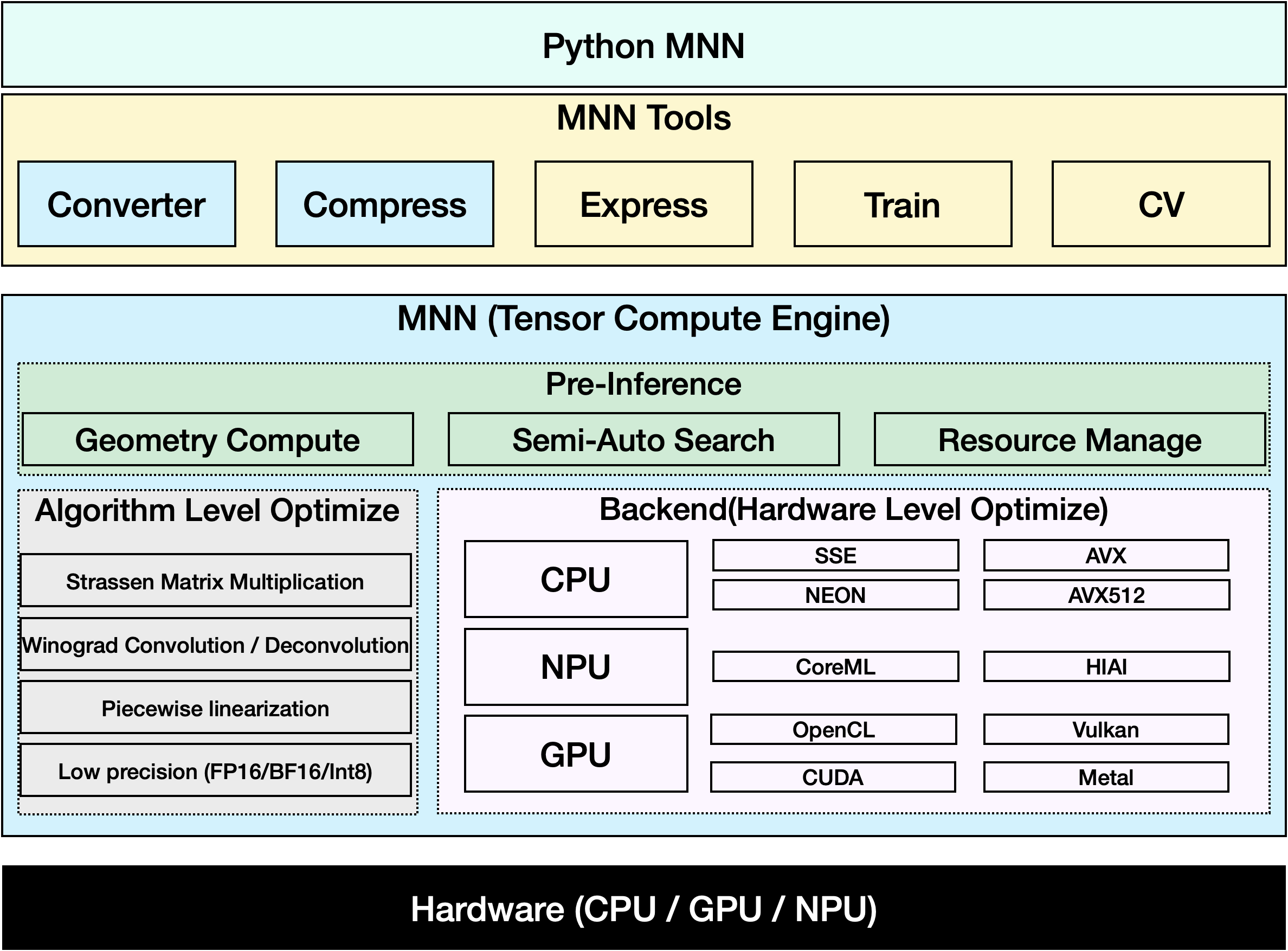
MNN là một framework deep learning hiệu quả và gọn nhẹ. Nó hỗ trợ suy luận và huấn luyện các mô hình deep learning và có hiệu suất hàng đầu trong ngành để suy luận và huấn luyện trên thiết bị. Hiện tại, MNN đã được tích hợp vào hơn 30 ứng dụng của Alibaba Inc, chẳng hạn như Taobao, Tmall, Youku, DingTalk, Xianyu, v.v., bao gồm hơn 70 kịch bản sử dụng như phát sóng trực tiếp, quay video ngắn, đề xuất tìm kiếm, tìm kiếm sản phẩm bằng hình ảnh, tiếp thị tương tác, phân phối vốn chủ sở hữu, kiểm soát rủi ro bảo mật. Ngoài ra, MNN còn được sử dụng trên các thiết bị nhúng, chẳng hạn như IoT.
Xem: Cách xuất Ultralytics YOLO26 sang định dạng MNN | Tăng tốc suy luận trên thiết bị di động📱
Xuất sang MNN: Chuyển đổi mô hình YOLO26 của bạn
Bạn có thể mở rộng khả năng tương thích của model và tính linh hoạt trong triển khai bằng cách chuyển đổi các model Ultralytics YOLO sang định dạng MNN. Việc chuyển đổi này tối ưu hóa các model của bạn cho môi trường di động và nhúng, đảm bảo hiệu suất hiệu quả trên các thiết bị có tài nguyên hạn chế.
Cài đặt
Để cài đặt các gói cần thiết, hãy chạy:
Cài đặt
# Install the required package for YOLO26 and MNN
pip install ultralytics
pip install MNN
Cách sử dụng
Tất cả các mô hình Ultralytics YOLO26 đều được thiết kế để hỗ trợ xuất ngay lập tức, giúp dễ dàng tích hợp chúng vào quy trình triển khai ưa thích của bạn. Bạn có thể xem danh sách đầy đủ các định dạng xuất được hỗ trợ và các tùy chọn cấu hình để chọn thiết lập tốt nhất cho ứng dụng của mình.
Cách sử dụng
from ultralytics import YOLO
# Load the YOLO26 model
model = YOLO("yolo26n.pt")
# Export the model to MNN format
model.export(format="mnn") # creates 'yolo26n.mnn'
# Load the exported MNN model
mnn_model = YOLO("yolo26n.mnn")
# Run inference
results = mnn_model("https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg")
# Export a YOLO26n PyTorch model to MNN format
yolo export model=yolo26n.pt format=mnn # creates 'yolo26n.mnn'
# Run inference with the exported model
yolo predict model='yolo26n.mnn' source='https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg'
Các đối số xuất
| Đối số | Loại | Mặc định | Mô tả |
|---|---|---|---|
format | str | 'mnn' | Dạng mục tiêu cho mô hình được xuất, xác định khả năng tương thích với các môi trường triển khai khác nhau. |
imgsz | int hoặc tuple | 640 | Kích thước hình ảnh mong muốn cho đầu vào của mô hình. Có thể là một số nguyên cho hình ảnh vuông hoặc một bộ giá trị (height, width) cho các kích thước cụ thể. |
half | bool | False | Cho phép lượng tử hóa FP16 (nửa độ chính xác), giảm kích thước mô hình và có khả năng tăng tốc độ suy luận trên phần cứng được hỗ trợ. |
int8 | bool | False | Kích hoạt lượng tử hóa INT8, nén thêm mô hình và tăng tốc độ suy luận với mức giảm độ chính xác tối thiểu, chủ yếu dành cho các thiết bị biên. |
batch | int | 1 | Chỉ định kích thước suy luận theo lô của mô hình xuất hoặc số lượng hình ảnh tối đa mà mô hình đã xuất sẽ xử lý đồng thời ở chế độ predict chế độ. |
device | str | None | Chỉ định thiết bị để xuất: GPU (device=0), CPU (device=cpu), MPS cho Apple silicon (device=mps). |
Để biết thêm chi tiết về quy trình xuất, hãy truy cập trang tài liệu Ultralytics về xuất.
Suy luận chỉ với MNN
Một chức năng chỉ dựa vào MNN để suy luận và tiền xử lý YOLO26 đã được triển khai, cung cấp cả phiên bản Python và C++ để dễ dàng triển khai trong mọi tình huống.
MNN
import argparse
import MNN
import MNN.cv as cv2
import MNN.numpy as np
def inference(model, img, precision, backend, thread):
config = {}
config["precision"] = precision
config["backend"] = backend
config["numThread"] = thread
rt = MNN.nn.create_runtime_manager((config,))
# net = MNN.nn.load_module_from_file(model, ['images'], ['output0'], runtime_manager=rt)
net = MNN.nn.load_module_from_file(model, [], [], runtime_manager=rt)
original_image = cv2.imread(img)
ih, iw, _ = original_image.shape
length = max((ih, iw))
scale = length / 640
image = np.pad(original_image, [[0, length - ih], [0, length - iw], [0, 0]], "constant")
image = cv2.resize(
image, (640, 640), 0.0, 0.0, cv2.INTER_LINEAR, -1, [0.0, 0.0, 0.0], [1.0 / 255.0, 1.0 / 255.0, 1.0 / 255.0]
)
image = image[..., ::-1] # BGR to RGB
input_var = image[None]
input_var = MNN.expr.convert(input_var, MNN.expr.NC4HW4)
output_var = net.forward(input_var)
output_var = MNN.expr.convert(output_var, MNN.expr.NCHW)
output_var = output_var.squeeze()
# output_var shape: [84, 8400]; 84 means: [cx, cy, w, h, prob * 80]
cx = output_var[0]
cy = output_var[1]
w = output_var[2]
h = output_var[3]
probs = output_var[4:]
# [cx, cy, w, h] -> [y0, x0, y1, x1]
x0 = cx - w * 0.5
y0 = cy - h * 0.5
x1 = cx + w * 0.5
y1 = cy + h * 0.5
boxes = np.stack([x0, y0, x1, y1], axis=1)
# ensure ratio is within the valid range [0.0, 1.0]
boxes = np.clip(boxes, 0, 1)
# get max prob and idx
scores = np.max(probs, 0)
class_ids = np.argmax(probs, 0)
result_ids = MNN.expr.nms(boxes, scores, 100, 0.45, 0.25)
print(result_ids.shape)
# nms result box, score, ids
result_boxes = boxes[result_ids]
result_scores = scores[result_ids]
result_class_ids = class_ids[result_ids]
for i in range(len(result_boxes)):
x0, y0, x1, y1 = result_boxes[i].read_as_tuple()
y0 = int(y0 * scale)
y1 = int(y1 * scale)
x0 = int(x0 * scale)
x1 = int(x1 * scale)
# clamp to the original image size to handle cases where padding was applied
x1 = min(iw, x1)
y1 = min(ih, y1)
print(result_class_ids[i])
cv2.rectangle(original_image, (x0, y0), (x1, y1), (0, 0, 255), 2)
cv2.imwrite("res.jpg", original_image)
if __name__ == "__main__":
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument("--model", type=str, required=True, help="the yolo26 model path")
parser.add_argument("--img", type=str, required=True, help="the input image path")
parser.add_argument("--precision", type=str, default="normal", help="inference precision: normal, low, high, lowBF")
parser.add_argument(
"--backend",
type=str,
default="CPU",
help="inference backend: CPU, OPENCL, OPENGL, NN, VULKAN, METAL, TRT, CUDA, HIAI",
)
parser.add_argument("--thread", type=int, default=4, help="inference using thread: int")
args = parser.parse_args()
inference(args.model, args.img, args.precision, args.backend, args.thread)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <MNN/ImageProcess.hpp>
#include <MNN/expr/Module.hpp>
#include <MNN/expr/Executor.hpp>
#include <MNN/expr/ExprCreator.hpp>
#include <MNN/expr/Executor.hpp>
#include <cv/cv.hpp>
using namespace MNN;
using namespace MNN::Express;
using namespace MNN::CV;
int main(int argc, const char* argv[]) {
if (argc < 3) {
MNN_PRINT("Usage: ./yolo26_demo.out model.mnn input.jpg [forwardType] [precision] [thread]\n");
return 0;
}
int thread = 4;
int precision = 0;
int forwardType = MNN_FORWARD_CPU;
if (argc >= 4) {
forwardType = atoi(argv[3]);
}
if (argc >= 5) {
precision = atoi(argv[4]);
}
if (argc >= 6) {
thread = atoi(argv[5]);
}
MNN::ScheduleConfig sConfig;
sConfig.type = static_cast<MNNForwardType>(forwardType);
sConfig.numThread = thread;
BackendConfig bConfig;
bConfig.precision = static_cast<BackendConfig::PrecisionMode>(precision);
sConfig.backendConfig = &bConfig;
std::shared_ptr<Executor::RuntimeManager> rtmgr = std::shared_ptr<Executor::RuntimeManager>(Executor::RuntimeManager::createRuntimeManager(sConfig));
if(rtmgr == nullptr) {
MNN_ERROR("Empty RuntimeManger\n");
return 0;
}
rtmgr->setCache(".cachefile");
std::shared_ptr<Module> net(Module::load(std::vector<std::string>{}, std::vector<std::string>{}, argv[1], rtmgr));
auto original_image = imread(argv[2]);
auto dims = original_image->getInfo()->dim;
int ih = dims[0];
int iw = dims[1];
int len = ih > iw ? ih : iw;
float scale = len / 640.0;
std::vector<int> padvals { 0, len - ih, 0, len - iw, 0, 0 };
auto pads = _Const(static_cast<void*>(padvals.data()), {3, 2}, NCHW, halide_type_of<int>());
auto image = _Pad(original_image, pads, CONSTANT);
image = resize(image, Size(640, 640), 0, 0, INTER_LINEAR, -1, {0., 0., 0.}, {1./255., 1./255., 1./255.});
image = cvtColor(image, COLOR_BGR2RGB);
auto input = _Unsqueeze(image, {0});
input = _Convert(input, NC4HW4);
auto outputs = net->onForward({input});
auto output = _Convert(outputs[0], NCHW);
output = _Squeeze(output);
// output shape: [84, 8400]; 84 means: [cx, cy, w, h, prob * 80]
auto cx = _Gather(output, _Scalar<int>(0));
auto cy = _Gather(output, _Scalar<int>(1));
auto w = _Gather(output, _Scalar<int>(2));
auto h = _Gather(output, _Scalar<int>(3));
std::vector<int> startvals { 4, 0 };
auto start = _Const(static_cast<void*>(startvals.data()), {2}, NCHW, halide_type_of<int>());
std::vector<int> sizevals { -1, -1 };
auto size = _Const(static_cast<void*>(sizevals.data()), {2}, NCHW, halide_type_of<int>());
auto probs = _Slice(output, start, size);
// [cx, cy, w, h] -> [y0, x0, y1, x1]
auto x0 = cx - w * _Const(0.5);
auto y0 = cy - h * _Const(0.5);
auto x1 = cx + w * _Const(0.5);
auto y1 = cy + h * _Const(0.5);
auto boxes = _Stack({x0, y0, x1, y1}, 1);
// ensure ratio is within the valid range [0.0, 1.0]
boxes = _Maximum(boxes, _Scalar<float>(0.0f));
boxes = _Minimum(boxes, _Scalar<float>(1.0f));
auto scores = _ReduceMax(probs, {0});
auto ids = _ArgMax(probs, 0);
auto result_ids = _Nms(boxes, scores, 100, 0.45, 0.25);
auto result_ptr = result_ids->readMap<int>();
auto box_ptr = boxes->readMap<float>();
auto ids_ptr = ids->readMap<int>();
auto score_ptr = scores->readMap<float>();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
auto idx = result_ptr[i];
if (idx < 0) break;
auto x0 = box_ptr[idx * 4 + 0] * scale;
auto y0 = box_ptr[idx * 4 + 1] * scale;
auto x1 = box_ptr[idx * 4 + 2] * scale;
auto y1 = box_ptr[idx * 4 + 3] * scale;
// clamp to the original image size to handle cases where padding was applied
x1 = std::min(static_cast<float>(iw), x1);
y1 = std::min(static_cast<float>(ih), y1);
auto class_idx = ids_ptr[idx];
auto score = score_ptr[idx];
rectangle(original_image, {x0, y0}, {x1, y1}, {0, 0, 255}, 2);
}
if (imwrite("res.jpg", original_image)) {
MNN_PRINT("result image write to `res.jpg`.\n");
}
rtmgr->updateCache();
return 0;
}
Tóm tắt
Trong hướng dẫn này, chúng tôi giới thiệu cách xuất mô hình Ultralytics YOLO26 sang MNN và sử dụng MNN để suy luận. Định dạng MNN cung cấp hiệu suất vượt trội cho các ứng dụng AI biên, lý tưởng để triển khai các mô hình thị giác máy tính trên các thiết bị có tài nguyên hạn chế.
Để biết thêm chi tiết về cách sử dụng, vui lòng tham khảo tài liệu MNN.
Câu hỏi thường gặp
Làm cách nào để xuất các mô hình Ultralytics YOLO26 sang định dạng MNN?
Để xuất mô hình Ultralytics YOLO26 của bạn sang định dạng MNN, hãy làm theo các bước sau:
Xuất
from ultralytics import YOLO
# Load the YOLO26 model
model = YOLO("yolo26n.pt")
# Export to MNN format
model.export(format="mnn") # creates 'yolo26n.mnn' with fp32 weight
model.export(format="mnn", half=True) # creates 'yolo26n.mnn' with fp16 weight
model.export(format="mnn", int8=True) # creates 'yolo26n.mnn' with int8 weight
yolo export model=yolo26n.pt format=mnn # creates 'yolo26n.mnn' with fp32 weight
yolo export model=yolo26n.pt format=mnn half=True # creates 'yolo26n.mnn' with fp16 weight
yolo export model=yolo26n.pt format=mnn int8=True # creates 'yolo26n.mnn' with int8 weight
Để biết các tùy chọn xuất chi tiết, hãy xem trang Xuất trong tài liệu.
Làm cách nào để dự đoán với một mô hình YOLO26 MNN đã xuất?
Để dự đoán với mô hình YOLO26 MNN đã xuất, hãy sử dụng predict function từ lớp YOLO.
Dự đoán
from ultralytics import YOLO
# Load the YOLO26 MNN model
model = YOLO("yolo26n.mnn")
# Export to MNN format
results = model("https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg") # predict with `fp32`
results = model("https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg", half=True) # predict with `fp16` if device support
for result in results:
result.show() # display to screen
result.save(filename="result.jpg") # save to disk
yolo predict model='yolo26n.mnn' source='https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg' # predict with `fp32`
yolo predict model='yolo26n.mnn' source='https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg' --half=True # predict with `fp16` if device support
Những nền tảng nào được hỗ trợ cho MNN?
MNN rất linh hoạt và hỗ trợ nhiều nền tảng khác nhau:
- Thiết bị di động: Android, iOS, Harmony.
- Hệ thống nhúng và thiết bị IoT: Các thiết bị như Raspberry Pi và NVIDIA Jetson.
- Máy tính để bàn và Máy chủ: Linux, Windows và macOS.
Làm thế nào để triển khai các mô hình Ultralytics YOLO26 MNN trên thiết bị di động?
Để triển khai các mô hình YOLO26 của bạn trên thiết bị di động:
- Xây dựng cho Android: Làm theo hướng dẫn MNN Android.
- Xây dựng cho iOS: Làm theo hướng dẫn MNN iOS.
- Xây dựng cho Harmony: Làm theo hướng dẫn MNN Harmony.