Esportazione MNN per modelli YOLO26 e distribuzione
MNN
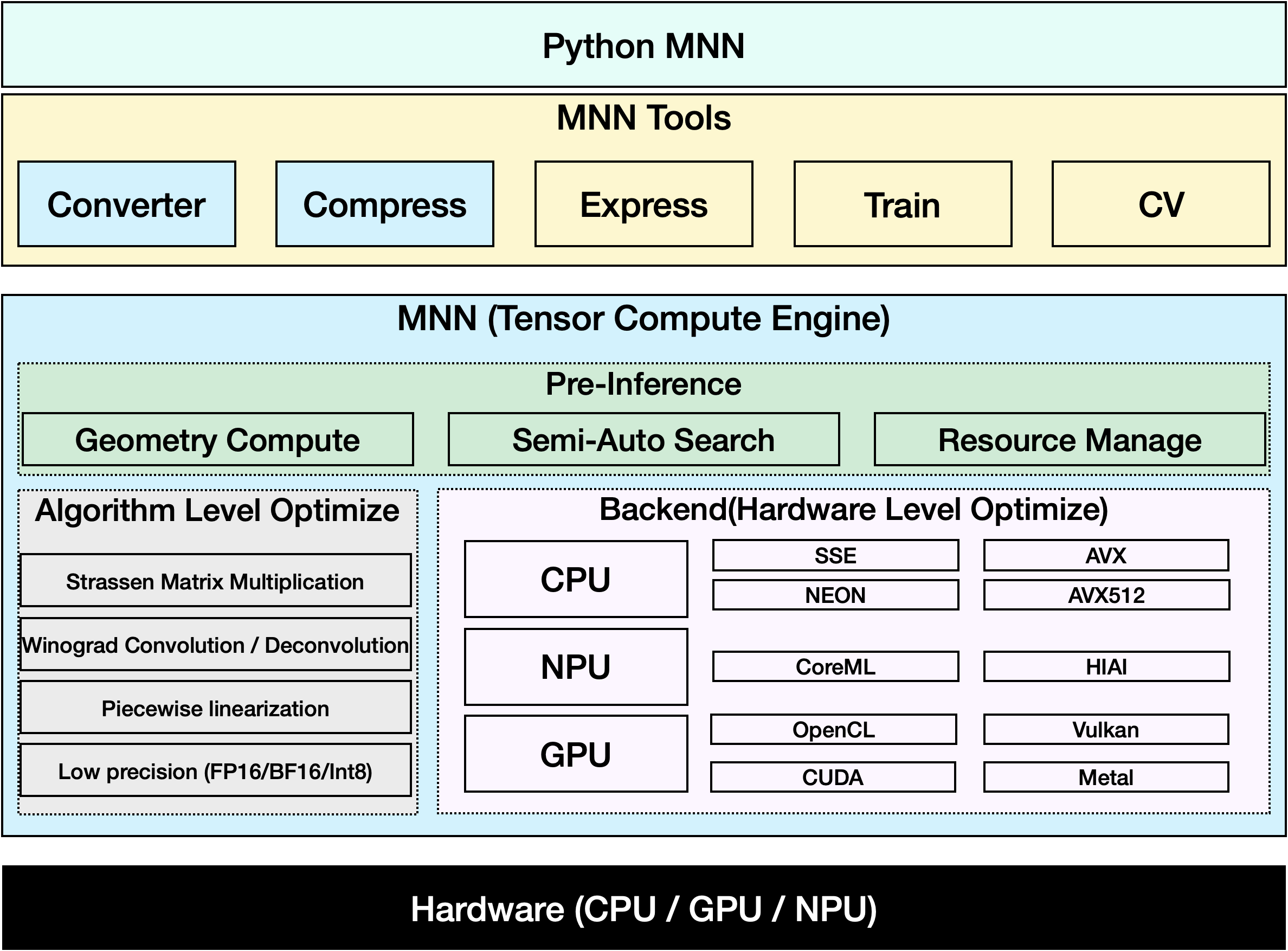
MNN è un framework di deep learning altamente efficiente e leggero. Supporta l'inferenza e l'addestramento di modelli di deep learning e offre prestazioni leader del settore per l'inferenza e l'addestramento on-device. Attualmente, MNN è stato integrato in più di 30 app di Alibaba Inc, come Taobao, Tmall, Youku, DingTalk, Xianyu, ecc., coprendo più di 70 scenari d'uso come live broadcast, acquisizione di brevi video, raccomandazione di ricerca, ricerca di prodotti tramite immagini, marketing interattivo, distribuzione di equity, controllo dei rischi per la sicurezza. Inoltre, MNN viene utilizzato anche su dispositivi embedded, come l'IoT.
Guarda: Come esportare Ultralytics YOLO26 nel formato MNN | Accelerare l'inferenza su dispositivi mobili📱
Esportazione in MNN: Conversione del tuo modello YOLO26
È possibile espandere la compatibilità del modello e la flessibilità di implementazione convertendo i modelli Ultralytics YOLO in formato MNN. Questa conversione ottimizza i tuoi modelli per ambienti mobili e embedded, garantendo prestazioni efficienti su dispositivi con risorse limitate.
Installazione
Per installare i pacchetti richiesti, esegui:
Installazione
# Install the required package for YOLO26 and MNN
pip install ultralytics
pip install MNN
Utilizzo
Tutti i modelli Ultralytics YOLO26 sono progettati per supportare l'esportazione out-of-the-box, rendendo facile integrarli nel flusso di lavoro di deployment preferito. È possibile visualizzare l'elenco completo dei formati di esportazione e delle opzioni di configurazione supportati per scegliere la configurazione migliore per la propria applicazione.
Utilizzo
from ultralytics import YOLO
# Load the YOLO26 model
model = YOLO("yolo26n.pt")
# Export the model to MNN format
model.export(format="mnn") # creates 'yolo26n.mnn'
# Load the exported MNN model
mnn_model = YOLO("yolo26n.mnn")
# Run inference
results = mnn_model("https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg")
# Export a YOLO26n PyTorch model to MNN format
yolo export model=yolo26n.pt format=mnn # creates 'yolo26n.mnn'
# Run inference with the exported model
yolo predict model='yolo26n.mnn' source='https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg'
Argomenti di esportazione
| Argomento | Tipo | Predefinito | Descrizione |
|---|---|---|---|
format | str | 'mnn' | Formato di destinazione per il modello esportato, che definisce la compatibilità con vari ambienti di distribuzione. |
imgsz | int oppure tuple | 640 | Dimensione dell'immagine desiderata per l'input del modello. Può essere un numero intero per immagini quadrate o una tupla (height, width) per dimensioni specifiche. |
half | bool | False | Abilita la quantizzazione FP16 (mezza precisione), riducendo le dimensioni del modello e potenzialmente accelerando l'inferenza su hardware supportato. |
int8 | bool | False | Attiva la quantizzazione INT8, comprimendo ulteriormente il modello e accelerando l'inferenza con una perdita di accuratezza minima, principalmente per i dispositivi edge. |
batch | int | 1 | Specifica la dimensione del batch di inferenza del modello di esportazione o il numero massimo di immagini che il modello esportato elaborerà contemporaneamente in modalità predict . |
device | str | None | Specifica il dispositivo per l'esportazione: GPU (device=0), CPU (device=cpu), MPS per Apple silicon (device=mps). |
Per maggiori dettagli sul processo di esportazione, visita la pagina della documentazione di Ultralytics sull'esportazione.
Inferenza Solo MNN
È stata implementata una funzione che si basa esclusivamente su MNN per l'inferenza e la pre-elaborazione di YOLO26, fornendo versioni sia Python che C++ per una facile distribuzione in qualsiasi scenario.
MNN
import argparse
import MNN
import MNN.cv as cv2
import MNN.numpy as np
def inference(model, img, precision, backend, thread):
config = {}
config["precision"] = precision
config["backend"] = backend
config["numThread"] = thread
rt = MNN.nn.create_runtime_manager((config,))
# net = MNN.nn.load_module_from_file(model, ['images'], ['output0'], runtime_manager=rt)
net = MNN.nn.load_module_from_file(model, [], [], runtime_manager=rt)
original_image = cv2.imread(img)
ih, iw, _ = original_image.shape
length = max((ih, iw))
scale = length / 640
image = np.pad(original_image, [[0, length - ih], [0, length - iw], [0, 0]], "constant")
image = cv2.resize(
image, (640, 640), 0.0, 0.0, cv2.INTER_LINEAR, -1, [0.0, 0.0, 0.0], [1.0 / 255.0, 1.0 / 255.0, 1.0 / 255.0]
)
image = image[..., ::-1] # BGR to RGB
input_var = image[None]
input_var = MNN.expr.convert(input_var, MNN.expr.NC4HW4)
output_var = net.forward(input_var)
output_var = MNN.expr.convert(output_var, MNN.expr.NCHW)
output_var = output_var.squeeze()
# output_var shape: [84, 8400]; 84 means: [cx, cy, w, h, prob * 80]
cx = output_var[0]
cy = output_var[1]
w = output_var[2]
h = output_var[3]
probs = output_var[4:]
# [cx, cy, w, h] -> [y0, x0, y1, x1]
x0 = cx - w * 0.5
y0 = cy - h * 0.5
x1 = cx + w * 0.5
y1 = cy + h * 0.5
boxes = np.stack([x0, y0, x1, y1], axis=1)
# ensure ratio is within the valid range [0.0, 1.0]
boxes = np.clip(boxes, 0, 1)
# get max prob and idx
scores = np.max(probs, 0)
class_ids = np.argmax(probs, 0)
result_ids = MNN.expr.nms(boxes, scores, 100, 0.45, 0.25)
print(result_ids.shape)
# nms result box, score, ids
result_boxes = boxes[result_ids]
result_scores = scores[result_ids]
result_class_ids = class_ids[result_ids]
for i in range(len(result_boxes)):
x0, y0, x1, y1 = result_boxes[i].read_as_tuple()
y0 = int(y0 * scale)
y1 = int(y1 * scale)
x0 = int(x0 * scale)
x1 = int(x1 * scale)
# clamp to the original image size to handle cases where padding was applied
x1 = min(iw, x1)
y1 = min(ih, y1)
print(result_class_ids[i])
cv2.rectangle(original_image, (x0, y0), (x1, y1), (0, 0, 255), 2)
cv2.imwrite("res.jpg", original_image)
if __name__ == "__main__":
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument("--model", type=str, required=True, help="the yolo26 model path")
parser.add_argument("--img", type=str, required=True, help="the input image path")
parser.add_argument("--precision", type=str, default="normal", help="inference precision: normal, low, high, lowBF")
parser.add_argument(
"--backend",
type=str,
default="CPU",
help="inference backend: CPU, OPENCL, OPENGL, NN, VULKAN, METAL, TRT, CUDA, HIAI",
)
parser.add_argument("--thread", type=int, default=4, help="inference using thread: int")
args = parser.parse_args()
inference(args.model, args.img, args.precision, args.backend, args.thread)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <MNN/ImageProcess.hpp>
#include <MNN/expr/Module.hpp>
#include <MNN/expr/Executor.hpp>
#include <MNN/expr/ExprCreator.hpp>
#include <MNN/expr/Executor.hpp>
#include <cv/cv.hpp>
using namespace MNN;
using namespace MNN::Express;
using namespace MNN::CV;
int main(int argc, const char* argv[]) {
if (argc < 3) {
MNN_PRINT("Usage: ./yolo26_demo.out model.mnn input.jpg [forwardType] [precision] [thread]\n");
return 0;
}
int thread = 4;
int precision = 0;
int forwardType = MNN_FORWARD_CPU;
if (argc >= 4) {
forwardType = atoi(argv[3]);
}
if (argc >= 5) {
precision = atoi(argv[4]);
}
if (argc >= 6) {
thread = atoi(argv[5]);
}
MNN::ScheduleConfig sConfig;
sConfig.type = static_cast<MNNForwardType>(forwardType);
sConfig.numThread = thread;
BackendConfig bConfig;
bConfig.precision = static_cast<BackendConfig::PrecisionMode>(precision);
sConfig.backendConfig = &bConfig;
std::shared_ptr<Executor::RuntimeManager> rtmgr = std::shared_ptr<Executor::RuntimeManager>(Executor::RuntimeManager::createRuntimeManager(sConfig));
if(rtmgr == nullptr) {
MNN_ERROR("Empty RuntimeManger\n");
return 0;
}
rtmgr->setCache(".cachefile");
std::shared_ptr<Module> net(Module::load(std::vector<std::string>{}, std::vector<std::string>{}, argv[1], rtmgr));
auto original_image = imread(argv[2]);
auto dims = original_image->getInfo()->dim;
int ih = dims[0];
int iw = dims[1];
int len = ih > iw ? ih : iw;
float scale = len / 640.0;
std::vector<int> padvals { 0, len - ih, 0, len - iw, 0, 0 };
auto pads = _Const(static_cast<void*>(padvals.data()), {3, 2}, NCHW, halide_type_of<int>());
auto image = _Pad(original_image, pads, CONSTANT);
image = resize(image, Size(640, 640), 0, 0, INTER_LINEAR, -1, {0., 0., 0.}, {1./255., 1./255., 1./255.});
image = cvtColor(image, COLOR_BGR2RGB);
auto input = _Unsqueeze(image, {0});
input = _Convert(input, NC4HW4);
auto outputs = net->onForward({input});
auto output = _Convert(outputs[0], NCHW);
output = _Squeeze(output);
// output shape: [84, 8400]; 84 means: [cx, cy, w, h, prob * 80]
auto cx = _Gather(output, _Scalar<int>(0));
auto cy = _Gather(output, _Scalar<int>(1));
auto w = _Gather(output, _Scalar<int>(2));
auto h = _Gather(output, _Scalar<int>(3));
std::vector<int> startvals { 4, 0 };
auto start = _Const(static_cast<void*>(startvals.data()), {2}, NCHW, halide_type_of<int>());
std::vector<int> sizevals { -1, -1 };
auto size = _Const(static_cast<void*>(sizevals.data()), {2}, NCHW, halide_type_of<int>());
auto probs = _Slice(output, start, size);
// [cx, cy, w, h] -> [y0, x0, y1, x1]
auto x0 = cx - w * _Const(0.5);
auto y0 = cy - h * _Const(0.5);
auto x1 = cx + w * _Const(0.5);
auto y1 = cy + h * _Const(0.5);
auto boxes = _Stack({x0, y0, x1, y1}, 1);
// ensure ratio is within the valid range [0.0, 1.0]
boxes = _Maximum(boxes, _Scalar<float>(0.0f));
boxes = _Minimum(boxes, _Scalar<float>(1.0f));
auto scores = _ReduceMax(probs, {0});
auto ids = _ArgMax(probs, 0);
auto result_ids = _Nms(boxes, scores, 100, 0.45, 0.25);
auto result_ptr = result_ids->readMap<int>();
auto box_ptr = boxes->readMap<float>();
auto ids_ptr = ids->readMap<int>();
auto score_ptr = scores->readMap<float>();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
auto idx = result_ptr[i];
if (idx < 0) break;
auto x0 = box_ptr[idx * 4 + 0] * scale;
auto y0 = box_ptr[idx * 4 + 1] * scale;
auto x1 = box_ptr[idx * 4 + 2] * scale;
auto y1 = box_ptr[idx * 4 + 3] * scale;
// clamp to the original image size to handle cases where padding was applied
x1 = std::min(static_cast<float>(iw), x1);
y1 = std::min(static_cast<float>(ih), y1);
auto class_idx = ids_ptr[idx];
auto score = score_ptr[idx];
rectangle(original_image, {x0, y0}, {x1, y1}, {0, 0, 255}, 2);
}
if (imwrite("res.jpg", original_image)) {
MNN_PRINT("result image write to `res.jpg`.\n");
}
rtmgr->updateCache();
return 0;
}
Riepilogo
In questa guida, presentiamo come esportare il modello Ultralytics YOLO26 in MNN e utilizzare MNN per l'inferenza. Il formato MNN offre prestazioni eccellenti per le applicazioni di edge AI, rendendolo ideale per la distribuzione di modelli di visione artificiale su dispositivi con risorse limitate.
Per ulteriori informazioni sull'utilizzo, consultare la documentazione MNN.
FAQ
Come si esportano i modelli Ultralytics YOLO26 nel formato MNN?
Per esportare il tuo modello Ultralytics YOLO26 nel formato MNN, segui questi passaggi:
Esportazione
from ultralytics import YOLO
# Load the YOLO26 model
model = YOLO("yolo26n.pt")
# Export to MNN format
model.export(format="mnn") # creates 'yolo26n.mnn' with fp32 weight
model.export(format="mnn", half=True) # creates 'yolo26n.mnn' with fp16 weight
model.export(format="mnn", int8=True) # creates 'yolo26n.mnn' with int8 weight
yolo export model=yolo26n.pt format=mnn # creates 'yolo26n.mnn' with fp32 weight
yolo export model=yolo26n.pt format=mnn half=True # creates 'yolo26n.mnn' with fp16 weight
yolo export model=yolo26n.pt format=mnn int8=True # creates 'yolo26n.mnn' with int8 weight
Per opzioni di esportazione dettagliate, consulta la pagina Esportazione nella documentazione.
Come si eseguono previsioni con un modello YOLO26 MNN esportato?
Per eseguire previsioni con un modello YOLO26 MNN esportato, usa la predict funzione dalla classe YOLO.
Predizione
from ultralytics import YOLO
# Load the YOLO26 MNN model
model = YOLO("yolo26n.mnn")
# Export to MNN format
results = model("https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg") # predict with `fp32`
results = model("https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg", half=True) # predict with `fp16` if device support
for result in results:
result.show() # display to screen
result.save(filename="result.jpg") # save to disk
yolo predict model='yolo26n.mnn' source='https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg' # predict with `fp32`
yolo predict model='yolo26n.mnn' source='https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg' --half=True # predict with `fp16` if device support
Quali piattaforme sono supportate per MNN?
MNN è versatile e supporta varie piattaforme:
- Mobile: Android, iOS, Harmony.
- Sistemi Embedded e dispositivi IoT: Dispositivi come Raspberry Pi e NVIDIA Jetson.
- Desktop e server: Linux, Windows e macOS.
Come posso distribuire i modelli Ultralytics YOLO26 MNN su dispositivi mobili?
Per distribuire i tuoi modelli YOLO26 su dispositivi mobili:
- Compilazione per Android: Segui la guida MNN Android.
- Compilazione per iOS: Segui la guida MNN iOS.
- Compilazione per Harmony: Segui la guida MNN Harmony.