YOLO26模型的MNN导出与部署
MNN
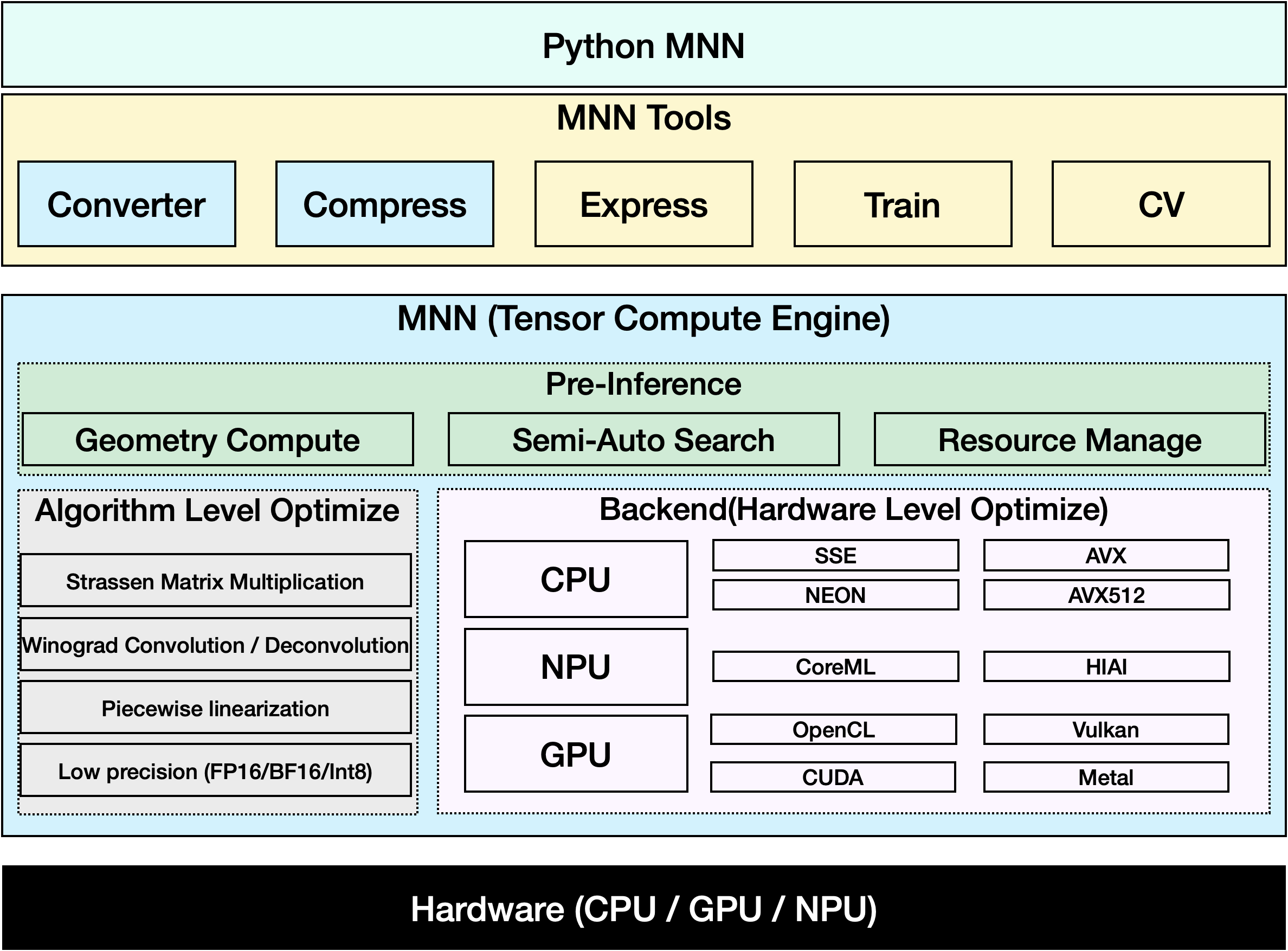
MNN 是一种高效且轻量级的深度学习框架。它支持深度学习模型的推理和训练,并在设备上的推理和训练方面具有行业领先的性能。目前,MNN 已集成到阿里巴巴集团的 30 多个应用程序中,例如淘宝、天猫、优酷、钉钉、闲鱼等,涵盖直播、短视频拍摄、搜索推荐、以图搜商品、互动营销、股权分配、安全风险控制等 70 多个使用场景。此外,MNN 还应用于嵌入式设备,如物联网。
观看: 如何将 Ultralytics YOLO26 导出为 MNN 格式 | 加速移动设备上的推理📱
导出到MNN:转换您的YOLO26模型
您可以通过将 Ultralytics YOLO 模型转换为 MNN 格式来扩展模型兼容性和部署灵活性。此转换优化了您的模型,使其适用于移动和嵌入式环境,从而确保在资源受限的设备上实现高效性能。
安装
要安装所需的软件包,请运行:
安装
# Install the required package for YOLO26 and MNN
pip install ultralytics
pip install MNN
用法
所有 Ultralytics YOLO26 模型 都设计为开箱即用地支持导出,从而可以轻松将其集成到您首选的部署工作流程中。您可以查看支持的导出格式和配置选项的完整列表,为您的应用程序选择最佳设置。
用法
from ultralytics import YOLO
# Load the YOLO26 model
model = YOLO("yolo26n.pt")
# Export the model to MNN format
model.export(format="mnn") # creates 'yolo26n.mnn'
# Load the exported MNN model
mnn_model = YOLO("yolo26n.mnn")
# Run inference
results = mnn_model("https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg")
# Export a YOLO26n PyTorch model to MNN format
yolo export model=yolo26n.pt format=mnn # creates 'yolo26n.mnn'
# Run inference with the exported model
yolo predict model='yolo26n.mnn' source='https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg'
导出参数
| 参数 | 类型 | 默认值 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
format | str | 'mnn' | 导出模型的目标格式,定义与各种部署环境的兼容性。 |
imgsz | int 或 tuple | 640 | 模型输入的所需图像大小。 可以是正方形图像的整数或元组 (height, width) 用于指定特定维度。 |
half | bool | False | 启用 FP16(半精度)量化,从而减小模型大小并可能加快受支持硬件上的推理速度。 |
int8 | bool | False | 激活 INT8 量化,进一步压缩模型并以最小的精度损失加快推理速度,主要用于边缘设备。 |
batch | int | 1 | 指定导出模型批处理推理大小或导出模型将并发处理的最大图像数量,在 predict 模式下。 |
device | str | None | 指定导出设备:GPU (device=0),CPU(device=cpu),适用于 Apple 芯片的 MPS(device=mps)。 |
有关导出过程的更多详细信息,请访问Ultralytics 文档页面上的导出。
仅 MNN 推理
已实现一个完全依赖 MNN 进行 YOLO26 推理和预处理的函数,提供 Python 和 C++ 版本,以便在任何场景下轻松部署。
MNN
import argparse
import MNN
import MNN.cv as cv2
import MNN.numpy as np
def inference(model, img, precision, backend, thread):
config = {}
config["precision"] = precision
config["backend"] = backend
config["numThread"] = thread
rt = MNN.nn.create_runtime_manager((config,))
# net = MNN.nn.load_module_from_file(model, ['images'], ['output0'], runtime_manager=rt)
net = MNN.nn.load_module_from_file(model, [], [], runtime_manager=rt)
original_image = cv2.imread(img)
ih, iw, _ = original_image.shape
length = max((ih, iw))
scale = length / 640
image = np.pad(original_image, [[0, length - ih], [0, length - iw], [0, 0]], "constant")
image = cv2.resize(
image, (640, 640), 0.0, 0.0, cv2.INTER_LINEAR, -1, [0.0, 0.0, 0.0], [1.0 / 255.0, 1.0 / 255.0, 1.0 / 255.0]
)
image = image[..., ::-1] # BGR to RGB
input_var = image[None]
input_var = MNN.expr.convert(input_var, MNN.expr.NC4HW4)
output_var = net.forward(input_var)
output_var = MNN.expr.convert(output_var, MNN.expr.NCHW)
output_var = output_var.squeeze()
# output_var shape: [84, 8400]; 84 means: [cx, cy, w, h, prob * 80]
cx = output_var[0]
cy = output_var[1]
w = output_var[2]
h = output_var[3]
probs = output_var[4:]
# [cx, cy, w, h] -> [y0, x0, y1, x1]
x0 = cx - w * 0.5
y0 = cy - h * 0.5
x1 = cx + w * 0.5
y1 = cy + h * 0.5
boxes = np.stack([x0, y0, x1, y1], axis=1)
# ensure ratio is within the valid range [0.0, 1.0]
boxes = np.clip(boxes, 0, 1)
# get max prob and idx
scores = np.max(probs, 0)
class_ids = np.argmax(probs, 0)
result_ids = MNN.expr.nms(boxes, scores, 100, 0.45, 0.25)
print(result_ids.shape)
# nms result box, score, ids
result_boxes = boxes[result_ids]
result_scores = scores[result_ids]
result_class_ids = class_ids[result_ids]
for i in range(len(result_boxes)):
x0, y0, x1, y1 = result_boxes[i].read_as_tuple()
y0 = int(y0 * scale)
y1 = int(y1 * scale)
x0 = int(x0 * scale)
x1 = int(x1 * scale)
# clamp to the original image size to handle cases where padding was applied
x1 = min(iw, x1)
y1 = min(ih, y1)
print(result_class_ids[i])
cv2.rectangle(original_image, (x0, y0), (x1, y1), (0, 0, 255), 2)
cv2.imwrite("res.jpg", original_image)
if __name__ == "__main__":
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument("--model", type=str, required=True, help="the yolo26 model path")
parser.add_argument("--img", type=str, required=True, help="the input image path")
parser.add_argument("--precision", type=str, default="normal", help="inference precision: normal, low, high, lowBF")
parser.add_argument(
"--backend",
type=str,
default="CPU",
help="inference backend: CPU, OPENCL, OPENGL, NN, VULKAN, METAL, TRT, CUDA, HIAI",
)
parser.add_argument("--thread", type=int, default=4, help="inference using thread: int")
args = parser.parse_args()
inference(args.model, args.img, args.precision, args.backend, args.thread)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <MNN/ImageProcess.hpp>
#include <MNN/expr/Module.hpp>
#include <MNN/expr/Executor.hpp>
#include <MNN/expr/ExprCreator.hpp>
#include <MNN/expr/Executor.hpp>
#include <cv/cv.hpp>
using namespace MNN;
using namespace MNN::Express;
using namespace MNN::CV;
int main(int argc, const char* argv[]) {
if (argc < 3) {
MNN_PRINT("Usage: ./yolo26_demo.out model.mnn input.jpg [forwardType] [precision] [thread]\n");
return 0;
}
int thread = 4;
int precision = 0;
int forwardType = MNN_FORWARD_CPU;
if (argc >= 4) {
forwardType = atoi(argv[3]);
}
if (argc >= 5) {
precision = atoi(argv[4]);
}
if (argc >= 6) {
thread = atoi(argv[5]);
}
MNN::ScheduleConfig sConfig;
sConfig.type = static_cast<MNNForwardType>(forwardType);
sConfig.numThread = thread;
BackendConfig bConfig;
bConfig.precision = static_cast<BackendConfig::PrecisionMode>(precision);
sConfig.backendConfig = &bConfig;
std::shared_ptr<Executor::RuntimeManager> rtmgr = std::shared_ptr<Executor::RuntimeManager>(Executor::RuntimeManager::createRuntimeManager(sConfig));
if(rtmgr == nullptr) {
MNN_ERROR("Empty RuntimeManger\n");
return 0;
}
rtmgr->setCache(".cachefile");
std::shared_ptr<Module> net(Module::load(std::vector<std::string>{}, std::vector<std::string>{}, argv[1], rtmgr));
auto original_image = imread(argv[2]);
auto dims = original_image->getInfo()->dim;
int ih = dims[0];
int iw = dims[1];
int len = ih > iw ? ih : iw;
float scale = len / 640.0;
std::vector<int> padvals { 0, len - ih, 0, len - iw, 0, 0 };
auto pads = _Const(static_cast<void*>(padvals.data()), {3, 2}, NCHW, halide_type_of<int>());
auto image = _Pad(original_image, pads, CONSTANT);
image = resize(image, Size(640, 640), 0, 0, INTER_LINEAR, -1, {0., 0., 0.}, {1./255., 1./255., 1./255.});
image = cvtColor(image, COLOR_BGR2RGB);
auto input = _Unsqueeze(image, {0});
input = _Convert(input, NC4HW4);
auto outputs = net->onForward({input});
auto output = _Convert(outputs[0], NCHW);
output = _Squeeze(output);
// output shape: [84, 8400]; 84 means: [cx, cy, w, h, prob * 80]
auto cx = _Gather(output, _Scalar<int>(0));
auto cy = _Gather(output, _Scalar<int>(1));
auto w = _Gather(output, _Scalar<int>(2));
auto h = _Gather(output, _Scalar<int>(3));
std::vector<int> startvals { 4, 0 };
auto start = _Const(static_cast<void*>(startvals.data()), {2}, NCHW, halide_type_of<int>());
std::vector<int> sizevals { -1, -1 };
auto size = _Const(static_cast<void*>(sizevals.data()), {2}, NCHW, halide_type_of<int>());
auto probs = _Slice(output, start, size);
// [cx, cy, w, h] -> [y0, x0, y1, x1]
auto x0 = cx - w * _Const(0.5);
auto y0 = cy - h * _Const(0.5);
auto x1 = cx + w * _Const(0.5);
auto y1 = cy + h * _Const(0.5);
auto boxes = _Stack({x0, y0, x1, y1}, 1);
// ensure ratio is within the valid range [0.0, 1.0]
boxes = _Maximum(boxes, _Scalar<float>(0.0f));
boxes = _Minimum(boxes, _Scalar<float>(1.0f));
auto scores = _ReduceMax(probs, {0});
auto ids = _ArgMax(probs, 0);
auto result_ids = _Nms(boxes, scores, 100, 0.45, 0.25);
auto result_ptr = result_ids->readMap<int>();
auto box_ptr = boxes->readMap<float>();
auto ids_ptr = ids->readMap<int>();
auto score_ptr = scores->readMap<float>();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
auto idx = result_ptr[i];
if (idx < 0) break;
auto x0 = box_ptr[idx * 4 + 0] * scale;
auto y0 = box_ptr[idx * 4 + 1] * scale;
auto x1 = box_ptr[idx * 4 + 2] * scale;
auto y1 = box_ptr[idx * 4 + 3] * scale;
// clamp to the original image size to handle cases where padding was applied
x1 = std::min(static_cast<float>(iw), x1);
y1 = std::min(static_cast<float>(ih), y1);
auto class_idx = ids_ptr[idx];
auto score = score_ptr[idx];
rectangle(original_image, {x0, y0}, {x1, y1}, {0, 0, 255}, 2);
}
if (imwrite("res.jpg", original_image)) {
MNN_PRINT("result image write to `res.jpg`.\n");
}
rtmgr->updateCache();
return 0;
}
总结
在本指南中,我们将介绍如何将 Ultralytics YOLO26 模型导出为 MNN 格式并使用 MNN 进行推理。MNN 格式为 边缘 AI 应用提供了出色的性能,使其成为在资源受限设备上部署计算机视觉模型的理想选择。
有关更多用法,请参考MNN 文档。
常见问题
如何将 Ultralytics YOLO26 模型导出为 MNN 格式?
要将您的 Ultralytics YOLO26 模型导出为 MNN 格式,请遵循以下步骤:
导出
from ultralytics import YOLO
# Load the YOLO26 model
model = YOLO("yolo26n.pt")
# Export to MNN format
model.export(format="mnn") # creates 'yolo26n.mnn' with fp32 weight
model.export(format="mnn", half=True) # creates 'yolo26n.mnn' with fp16 weight
model.export(format="mnn", int8=True) # creates 'yolo26n.mnn' with int8 weight
yolo export model=yolo26n.pt format=mnn # creates 'yolo26n.mnn' with fp32 weight
yolo export model=yolo26n.pt format=mnn half=True # creates 'yolo26n.mnn' with fp16 weight
yolo export model=yolo26n.pt format=mnn int8=True # creates 'yolo26n.mnn' with int8 weight
有关详细的导出选项,请查看文档中的导出页面。
如何使用已导出的 YOLO26 MNN 模型进行预测?
要使用已导出的 YOLO26 MNN 模型进行预测,请使用 predict YOLO 类中的 function。
预测
from ultralytics import YOLO
# Load the YOLO26 MNN model
model = YOLO("yolo26n.mnn")
# Export to MNN format
results = model("https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg") # predict with `fp32`
results = model("https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg", half=True) # predict with `fp16` if device support
for result in results:
result.show() # display to screen
result.save(filename="result.jpg") # save to disk
yolo predict model='yolo26n.mnn' source='https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg' # predict with `fp32`
yolo predict model='yolo26n.mnn' source='https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg' --half=True # predict with `fp16` if device support
MNN 支持哪些平台?
MNN 用途广泛,支持多种平台:
- 移动端: Android、iOS、Harmony。
- 嵌入式系统和 IoT 设备:诸如 Raspberry Pi 和 NVIDIA Jetson 之类的设备。
- 桌面和服务器: Linux、Windows 和 macOS。
如何在移动设备上部署 Ultralytics YOLO26 MNN 模型?
要在移动设备上部署您的YOLO26模型:
- Android 构建: 请遵循 MNN Android 指南。
- iOS 构建: 请遵循 MNN iOS 指南。
- Harmony 构建: 请遵循 MNN Harmony 指南。